
Welcome to the ultimate guide to hydroponics for beginners! If you’ve ever dreamed of growing your own fresh and healthy produce but don’t have the space or resources for a traditional garden, hydroponics might just be the solution you’ve been looking for. This innovative and efficient method of gardening allows you to cultivate plants without soil, using water and nutrient-rich solutions instead. Whether you’re an urban dweller with limited outdoor space or simply want to explore a more sustainable way of growing your own food, this step-by-step guide will walk you through the basics of hydroponics. From setting up your own hydroponic system to selecting the right plants and providing them with the necessary nutrients, we’ll cover everything you need to know to get started on your hydroponic journey. Get ready to discover the exciting world of hydroponics and unlock your green thumb, all while reaping the rewards of fresh, homegrown produce.
What is hydroponics?
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants without soil. Instead, plants are grown in a nutrient-rich water solution that provides all the essential elements for growth. This method allows for precise control of the plant’s environment, including the amount of water, nutrients, and light it receives. By removing the need for soil, hydroponics offers several advantages over traditional gardening methods.
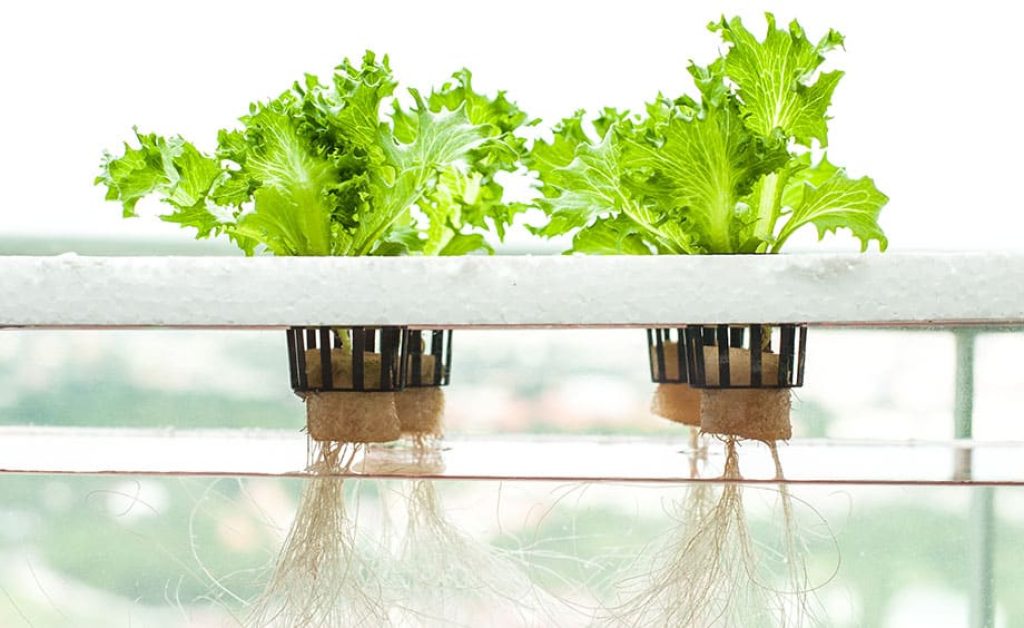

One of the key benefits of hydroponics is its ability to maximize space utilization. Without the need for soil, plants can be grown in a much smaller area, making hydroponics a great option for urban dwellers or anyone with limited outdoor space. Additionally, the controlled environment of hydroponics allows for year-round cultivation, regardless of the weather conditions outside. This means you can enjoy fresh produce even during the winter months.
In terms of resource efficiency, hydroponics is a game-changer. Unlike traditional gardening, where water is lost through evaporation and drainage, hydroponics recirculates water, drastically reducing water waste. Additionally, the precise control of nutrient delivery in hydroponics ensures that plants receive exactly what they need, minimizing fertilizer usage. This makes hydroponics a sustainable and environmentally friendly option for growing your own food.
Benefits of hydroponics
Hydroponics offers a wide range of benefits that make it an attractive option for both beginners and experienced gardeners alike. Here are some of the key advantages of hydroponic gardening:

1. **Maximized space utilization**: With hydroponics, you can grow more plants in a smaller area compared to traditional gardening methods. This is especially beneficial for urban gardeners or those with limited outdoor space.
2. **Year-round cultivation**: Unlike traditional gardening, hydroponics allows for year-round cultivation. By creating an ideal growing environment indoors, you can enjoy fresh produce even during the winter months.
3. **Water efficiency**: Hydroponics is highly water-efficient as it recirculates water, minimizing waste. With precise control over water delivery, you can ensure that plants receive the right amount of moisture without any excess.
4. **Nutrient control**: In hydroponics, you have complete control over the nutrient solution that plants receive. This allows you to provide them with the exact balance of essential elements they need for optimal growth.
5. **Faster growth and higher yields**: With the right setup, hydroponic plants can grow up to 50% faster than those grown in soil. Additionally, hydroponics often results in higher yields, meaning you can enjoy more abundant harvests.
6. **Pest and disease control**: The controlled environment of hydroponics reduces the risk of pests and diseases. Without soil, many common garden pests and diseases are eliminated, resulting in healthier plants.
7. **Sustainable and eco-friendly**: Hydroponics minimizes water and fertilizer usage, making it a sustainable and environmentally friendly option for growing your own food.
By harnessing the power of hydroponics, you can enjoy the benefits of fresh and healthy produce, regardless of your gardening experience or available space.
Hydroponics vs. traditional soil gardening
Hydroponics and traditional soil gardening are two distinct methods of plant cultivation, each with its own set of advantages and challenges. Understanding the differences between these two approaches can help you make an informed decision about which method suits your gardening needs.
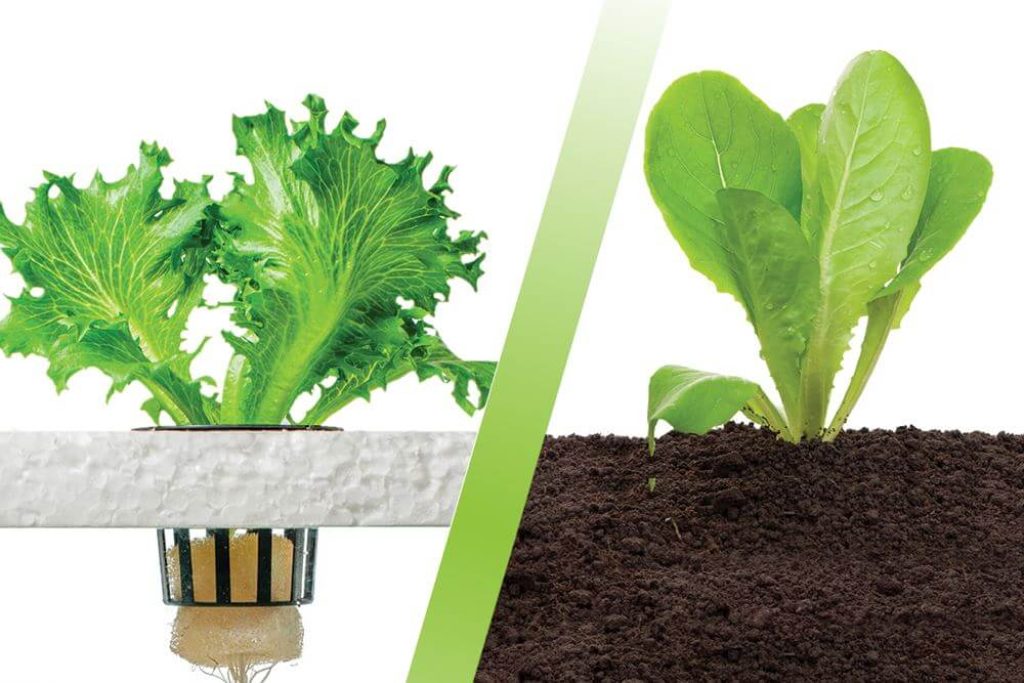

**1. Growing medium:** In traditional soil gardening, plants rely on the soil as a growing medium. The soil provides the necessary support for the roots and acts as a reservoir for water and nutrients. On the other hand, hydroponics utilizes inert growing mediums such as perlite, vermiculite, or coconut coir. These mediums provide support to the plants while allowing for optimal absorption of the nutrient solution. The absence of soil in hydroponics eliminates the risk of soil-borne diseases and pests.
**2. Nutrient delivery:** In traditional gardening, plants obtain their nutrients from the soil. The nutrients are present in the soil in various forms and are absorbed by the roots through a process called ion exchange. In hydroponics, the nutrients are dissolved in a water solution, which is then directly delivered to the roots. This allows for precise control over nutrient delivery, ensuring that the plants receive the optimal balance of nutrients for optimal growth.
**3. Water management:** Traditional soil gardening requires regular watering to ensure that the plants receive adequate moisture. However, overwatering or underwatering can lead to root rot or nutrient deficiencies respectively. Hydroponics, on the other hand, allows for precise control over water delivery. The water used in a hydroponic system is recirculated, reducing water consumption and minimizing the risk of over or underwatering.
**4. Space requirements:** Traditional soil gardening typically requires a significant amount of space, as plants need ample room for their roots to spread and grow. Hydroponics, on the other hand, offers the advantage of space-saving cultivation. Since hydroponic systems can be set up vertically or in compact configurations, they require significantly less space compared to traditional gardens. This makes hydroponics an ideal solution for those with limited gardening space.
**5. Pest and disease control:** Traditional soil-based gardens are susceptible to a wide range of pests, diseases, and weeds. These issues can significantly impact plant health and productivity. Hydroponics, on the other hand, provides a controlled environment that minimizes these problems. With hydroponics, there is no risk of soil-borne diseases, and pests are easier to detect and manage. This reduces the need for harmful pesticides and herbicides, resulting in healthier and safer produce.
While both methods have their merits, hydroponics offers several distinct advantages that make it an attractive option for modern gardeners. Now that we have explored the differences between hydroponics and traditional gardening, let’s take a closer look at how hydroponics works and the essential components of a hydroponic system.
Types of hydroponic systems
There are several different types of hydroponic systems to choose from, each with its own advantages and considerations. Understanding the different options will help you select the system that best suits your needs and preferences. Here are some of the most common types of hydroponic systems:
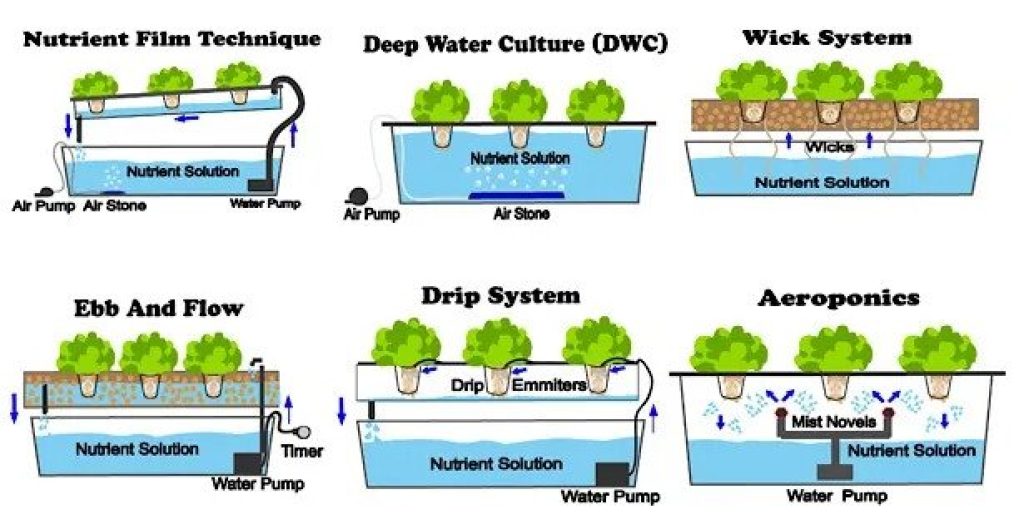
1. **Deep Water Culture (DWC)**: In a Deep Water Culture system, plants are suspended in a nutrient-rich water solution with their roots submerged. An air pump is used to provide oxygen to the roots, promoting healthy growth. This system is relatively simple and inexpensive, making it a popular choice for beginners.
2. **Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)**: The Nutrient Film Technique involves a thin film of nutrient solution flowing over the roots of the plants. The roots are exposed to air, providing oxygen, while the constant flow of nutrients ensures their uptake. NFT systems are popular for their simplicity and efficiency.
3. **Drip System**: Drip systems deliver nutrient solution to the plants through a network of tubes and drippers. This allows for precise control of the nutrient delivery, making it suitable for a wide range of plants. Drip systems can be automated, reducing the need for constant monitoring.
4. **Ebb and Flow**: Also known as flood and drain systems, Ebb and Flow systems periodically flood the plant roots with nutrient solution and then drain it away. This cycle ensures that plants receive both nutrients and oxygen, promoting healthy growth. Ebb and Flow systems are versatile and can be used with a variety of growing mediums.
5. **Aeroponics**: In an Aeroponics system, plant roots are suspended in the air and periodically misted with a nutrient solution. This method provides maximum oxygenation and nutrient uptake, resulting in rapid growth. Aeroponics is a highly efficient system but requires more technical expertise.
Choosing the right hydroponic system for your needs
Selecting the right hydroponic system is crucial for the success of your hydroponic garden. Consider the following factors when choosing a system:
1. **Available space**: Assess the amount of space you have available for your hydroponic garden. Some systems, like Deep Water Culture, require more vertical space, while others, like Nutrient Film Technique, are more suitable for limited space.
2. **Budget**: Determine your budget for setting up the hydroponic system. Some systems, like Deep Water Culture, are relatively inexpensive and easy to set up, while others, like Aeroponics, require more investment.
3. **Plant selection**: Consider the types of plants you want to grow. Some plants, like leafy greens, thrive in Deep Water Culture or Nutrient Film Technique systems, while others, like tomatoes, may require a more complex system like Aeroponics.
4. **Maintenance**: Assess your willingness and ability to maintain the hydroponic system. Some systems, like Drip or Ebb and Flow, require more regular maintenance and monitoring, while others, like Deep Water Culture, are relatively low-maintenance.
By considering these factors, you can select a hydroponic system that suits your specific needs and preferences. Remember that it’s always a good idea to start with a simple system if you’re new to hydroponics and gradually expand as you gain experience.
Setting up your hydroponic system
Once you’ve chosen the right hydroponic system for your needs, it’s time to set up your garden. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
1. **Choose a location**: Select a suitable location for your hydroponic system. Ideally, it should be an area with access to natural light or a space where you can install artificial lighting.
2. **Prepare the space**: Clean and disinfect the area where you’ll be setting up your hydroponic system. This will help prevent the growth of algae or harmful bacteria.
3. **Assemble the system**: Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to assemble your chosen hydroponic system. Make sure all components are securely connected and functioning properly.
4. **Install lighting**: If you’re growing plants indoors or in a space with limited natural light, install grow lights to provide the necessary light spectrum for plant growth. LED grow lights are a popular and energy-efficient option.
5. **Prepare the nutrient solution**: Mix the appropriate amount of nutrient solution according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure that the pH level of the solution is within the optimal range for your plants.
6. **Plant the seedlings**: Place the seedlings or seeds into the growing medium or the designated slots in your hydroponic system. Ensure that the roots are in contact with the nutrient solution or the growing medium.
7. **Monitor and adjust**: Regularly monitor the pH level and nutrient concentration of the solution. Adjust as needed to maintain optimal growing conditions for your plants.
8. **Maintain the system**: Keep an eye on the water levels, temperature, and humidity within your hydroponic system. Clean and maintain the system regularly to prevent the buildup of algae or debris.
By following these steps, you’ll have your hydroponic system set up and ready to grow healthy and thriving plants. Remember to regularly check on your plants, provide the necessary care, and adjust the environment as needed to ensure their success.
Hydroponic gardening supplies and equipment
To start with hydroponic gardening, there are several supplies and pieces of equipment you will need:
- Hydroponic System: There are many types of hydroponic systems, such as Deep Water Culture (DWC), Nutrient Film Technique (NFT), Ebb and Flow, and Aeroponics. The choice depends on your space, budget, and the types of plants you want to grow.
- Reservoir: This is where the nutrient solution is stored. The size of the reservoir will depend on the size of your hydroponic system.
- Water Pump: A water pump is needed to move the nutrient solution from the reservoir to the plants. Make sure to get one that is suitable for the size of your hydroponic system.
- Air Pump and Air Stones: These are used in some hydroponic systems to provide oxygen to the roots of the plants. The air pump pumps air into the reservoir, and the air stones diffuse the air into small bubbles, increasing the oxygenation of the nutrient solution.
- Growing Medium: Unlike traditional gardening, hydroponics doesn’t use soil. Instead, you’ll need a soilless growing medium like Rockwool, coconut coir, perlite, clay pebbles, or vermiculite.
- Nutrient Solution: Plants need nutrients to grow, and in hydroponics, these are provided directly in the water. You’ll need a hydroponic-grade nutrient solution that contains all the essential nutrients your plants need.
- pH and EC/TDS Meters: These are necessary to monitor the pH and nutrient concentration of your solution. Maintaining the right pH and nutrient levels is essential for plant health and growth.
- pH Adjusters: These are used to correct the pH of your nutrient solution if it falls outside the optimal range for your plants.
- Lights: If you’re growing indoors, you’ll need grow lights. There are several types, such as fluorescent, HID (High-Intensity Discharge), LED, and others. The best choice depends on your needs, budget, and the types of plants you’re growing.
- Timer: Many hydroponic systems require a timer to control the watering cycle and, if you’re using artificial lights, the light/dark cycle.
- Seeds or Plants: Finally, you’ll need something to grow! Many types of plants can be grown hydroponically, but some are easier for beginners than others. Some common choices include lettuce, herbs, tomatoes, peppers, and strawberries.
- Grow Trays/Net Pots: Depending on your system, you might need trays or pots to hold your plants. Net pots are particularly popular in hydroponics because they allow the nutrient solution to easily reach the roots of your plants.
Remember that these are the basics. Depending on your specific system and the plants you choose to grow, there may be other supplies and equipment that you’ll need.
Nutrient solutions for hydroponics
In hydroponics, plants rely on nutrient solutions to provide them with the essential elements necessary for growth. These nutrient solutions contain a balanced mix of macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and micronutrients (iron, manganese, zinc, etc.) that plants need in varying amounts. Here are some key considerations when it comes to nutrient solutions in hydroponics:
1. **pH level**: The pH level of the nutrient solution is crucial for nutrient availability to the plants. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic pH range between 5.5 and 6.5. Regularly monitor and adjust the pH level of the solution using pH testing kits or meters.
2. **EC/TDS**: Electrical conductivity (EC) or total dissolved solids (TDS) measures the concentration of dissolved nutrients in the solution. It is important to monitor and maintain the EC/TDS levels within the optimal range for your plants, as excessive or deficient nutrient concentrations can harm plant growth.
3. **Nutrient ratios**: Different plants have varying nutrient requirements at different stages of growth. Most hydroponic nutrient solutions come with instructions on the appropriate ratios for different growth stages. Follow these guidelines to ensure your plants receive the right nutrients at the right time.
4. **Water quality**: The quality of the water you use to make the nutrient solution can affect plant growth. Ideally, use clean, filtered water or tap water that has been dechlorinated. Avoid using water with high levels of contaminants or minerals that can negatively impact plant health.
5. **Nutrient solution management**: Regularly monitor the nutrient solution’s pH, EC/TDS, and nutrient levels to ensure optimal plant growth. Test the solution at least once a week and make adjustments as needed.
By providing your plants with a well-balanced and properly managed nutrient solution, you’ll help them thrive and achieve their full growth potential in your hydroponic garden.
Plant selection for hydroponics
Hydroponics offers a wide range of possibilities when it comes to plant selection. While most plants can be grown hydroponically, some are better suited for this method than others. Here are some popular choices for hydroponic gardening:
1. **Leafy greens**: Lettuce, spinach, kale, and other leafy greens are excellent choices for hydroponics. They grow quickly and can be harvested in a short period of time. Leafy greens thrive in systems like Deep Water Culture and Nutrient Film Technique.
2. **Herbs**: Basil, parsley, cilantro, and other herbs are well-suited for hydroponic cultivation. They require less space and have a high demand in the culinary world. Herbs can be grown in various hydroponic systems, such as NFT or Drip.
3. **Tomatoes**: Tomatoes are a popular choice for hydroponic gardening due to their high yield potential. They require more space and support, making systems like Ebb and Flow or Aeroponics ideal for their growth.
4. **Strawberries**: Strawberries grow exceptionally well in hydroponic systems, producing delicious and juicy fruits. They are often grown in vertical systems, like Tower Gardens, to maximize space utilization.
5. **Peppers**: Peppers, both sweet and hot varieties, thrive in hydroponic environments. They require a longer growing season, making hydroponics a great option for extending the growing period.
6. **Cucumbers**: Cucumbers can be successfully grown in hydroponic systems, producing crisp and refreshing fruits. Trellising is often necessary to support the plants’ growth.
These are just a few examples of the many plants that can be grown hydroponically. When selecting plants for your hydroponic garden, consider factors such as space requirements, growth characteristics, and your personal preferences.
Maintaining your hydroponic garden
Maintaining a hydroponic garden requires regular attention and care to ensure optimal plant growth. Here are some key maintenance tasks to keep in mind:
1. **Monitoring**: Regularly monitor the pH level, EC/TDS, and nutrient concentrations of the solution. This can be done using pH testing kits, EC/TDS meters, and nutrient testing kits. Maintain records of these measurements to track any changes or trends.
2. **Watering**: Check the water level in your hydroponic system regularly and top it up as needed. Ensure that the water level is sufficient for the roots to have access to the nutrient solution.
3. **Cleaning**: Clean your hydroponic system regularly to prevent the buildup of algae, debris, or pathogens. This includes cleaning the reservoir, pumps, and any other components. Use a mild detergent or a hydrogen peroxide solution for cleaning.
4. **Pruning and training**: Prune and train your plants as they grow to encourage healthy development and prevent overcrowding. This includes removing dead or damaged leaves, pinching off excessive growth, and providing support for vining plants.
5. **Pest and disease control**: Despite the controlled environment of hydroponics, pests and diseases can still be a concern. Regularly inspect your plants for any signs of pests or diseases and take appropriate measures to control them. This may include applying organic pest control methods or using beneficial insects.
6. **Lighting adjustments**: If you’re using artificial lighting, monitor the light intensity and adjust the distance from your plants as necessary. Different plants have different light requirements, so ensure that they are getting the right amount of light. Regularly check and replace bulbs as they lose their effectiveness over time. If you’re using a timer, adjust the light/dark cycle according to the specific needs of your plants, typically following their natural growth cycles.
7. **Nutrient replenishment**: The nutrient solution needs to be replenished regularly to ensure the plants are receiving the necessary nutrients for growth. This usually involves draining the old nutrient solution and replacing it with fresh solution. Monitor your plants’ growth and adjust the nutrient mix as required.
8. **Temperature control**: Different plants have different temperature needs, so it is essential to maintain an optimal temperature in your hydroponic system. Monitor the ambient temperature and, if needed, use heaters or coolers to maintain the desired temperature.
9. **Humidity and air circulation**: It’s also necessary to monitor and manage the humidity level within your system. Proper air circulation is also crucial to prevent mold and diseases, and to ensure your plants get enough carbon dioxide for photosynthesis. Use fans, humidifiers, or dehumidifiers as needed.
10. **Regular inspections**: Finally, do regular thorough inspections of your whole system, from plants to equipment, to detect any potential issues early on. This includes checking the roots for rot, looking for any leaks or malfunctions in the system, and ensuring that pumps and timers are working correctly. Promptly address any issues you discover to keep your hydroponic garden thriving.
Common challenges in hydroponics and how to overcome them
While hydroponic systems offer many advantages, there can also be challenges associated with this method of gardening. Some of the most common challenges and how to overcome them are:
- Nutrient Imbalance: As discussed earlier, managing the nutrient balance is crucial. Plants can show signs of deficiency or toxicity if the nutrients are not balanced correctly. Using a high-quality nutrient solution, regularly testing the nutrient levels, and adjusting as necessary can help avoid this problem.
- pH Fluctuation: The pH level of your nutrient solution can greatly affect how well plants absorb nutrients. If the pH fluctuates outside the optimal range, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. Regularly test the pH and use pH adjusters as necessary to keep it stable.
- Disease and Pests: Even in a controlled environment, pests and diseases can still be a problem. Regularly inspect your plants for signs of pests or disease. Using biological pest control, like beneficial insects, or plant-safe pesticides can help manage pests. For diseases, prevention is best – keep the system clean, ensure good air circulation, and remove and dispose of any infected plants promptly.
- System Failure: In a hydroponic system, plants rely entirely on the system to deliver water and nutrients. Any failure in the system, like a pump failure, can quickly lead to plant stress or death. Regularly check and maintain your system to prevent failures. Having a backup plan, like an extra pump, can also be a good idea.
- Algae Growth: Algae thrive in nutrient-rich, moist environments – just like a hydroponic system. Algae can compete with your plants for nutrients and clog up your system. To prevent algae growth, keep your system clean, avoid letting light get into your nutrient reservoir, and regularly replace your nutrient solution.
- High Initial Costs: Setting up a hydroponic system can be expensive compared to traditional gardening. However, over time, the higher yields and efficiencies can make up for these costs. Start small, and expand your system as you gain experience and confidence.
- Knowledge and Experience: Hydroponic gardening can be complex and intimidating for beginners. It requires a good understanding of plant needs and system management. Start with easier plants, use reliable resources to learn, and don’t be discouraged by initial challenges.
Remember, every challenge is an opportunity to learn and improve. With careful attention and management, you can overcome these challenges and successfully grow plants hydroponically.
Tips for successful hydroponic gardening
Here are some tips to make your hydroponic gardening experience more successful:
- Education: Before starting, educate yourself about hydroponic systems, plant requirements, nutrient solutions, and potential issues you may face. Read books, follow reliable online resources, join community forums, or even take a local class if available. This will prepare you for the challenges that might come along the way.
- Start Small: If you’re new to hydroponics, start with a small system and a few easy-to-grow plants. This will allow you to learn the basics without being overwhelmed, and you can expand your system as you gain experience and confidence.
- Use the Right Equipment: Quality equipment will make your hydroponic gardening experience much smoother. This includes everything from the hydroponic system itself to pH and EC/TDS meters, quality lights for indoor gardening, and good-quality nutrient solutions.
- Monitor Regularly: Regular monitoring of your system is crucial for success in hydroponics. Check the pH and nutrient levels often, monitor the health of your plants, and inspect your system for any signs of trouble like algae growth or equipment malfunction.
- Maintain Cleanliness: Keep your system clean to prevent the buildup of pathogens or algae. This includes cleaning the reservoir, pumps, and other components regularly.
- Proper Lighting: If you’re growing indoors, invest in quality grow lights and ensure that your plants are getting the right amount of light. Adjust the light intensity and the distance from your plants as necessary.
- Climate Control: Maintain the optimal temperature and humidity levels for your plants. Too much heat or cold, or incorrect humidity, can stress your plants and affect their growth.
- Proper Plant Selection: Not all plants are suitable for hydroponic systems. Research and select plants that are known to grow well in hydroponics, especially if you’re a beginner.
- Patience and Persistence: Don’t be discouraged by initial setbacks. Hydroponic gardening has a learning curve, but with patience and persistence, you will get the hang of it.
- Join a Community: Joining a community of hydroponic growers, either online or locally, can provide invaluable support and advice. It can also make your gardening experience more enjoyable.
Remember, every garden and gardener is unique, so don’t be afraid to experiment and find what works best for you and your plants. Happy gardening!
Hydroponics resources and communities
If you’re looking to delve deeper into the world of hydroponics, there are numerous resources and communities available to help you along your journey. Here are a few recommendations:
Books and Manuals:
- “Hydroponics: A Practical Guide for the Soilless Grower” by J. Benton Jones Jr.
- “Hydroponic Food Production: A Definitive Guidebook for the Advanced Home Gardener and the Commercial Hydroponic Grower” by Howard M. Resh.
- “DIY Hydroponic Gardens: How to Design and Build an Inexpensive System for Growing Plants in Water” by Tyler Baras.
Online Learning Platforms:
- Coursera: Offers various courses on hydroponics and urban agriculture.
- Udemy: There are many hydroponics courses by expert growers that cater to both beginners and advanced users.
Forums and Online Communities:
- Reddit: Subreddits such as /r/Hydro and /r/Hydroponics are communities of hydroponic growers where you can ask questions, share your progress, and learn from others’ experiences.
- The Hydroponic Garden Secret: An active online forum that discusses different aspects of hydroponics.
- Hydroponic Gardening & More with Brent: This is a Facebook group with a large community of hydroponic enthusiasts.
Blogs and Websites:
- Epic Gardening: Kevin Espiritu’s website covers all aspects of urban agriculture, including a lot of helpful information on hydroponics.
- Just 4 Growers: A resource-rich website dedicated to indoor gardening, hydroponics included.
- Hydroponics-Simplified: A comprehensive site that walks you through all the basics of hydroponics.
YouTube Channels:
- Jeb Gardener: Offers a humorous and informative look at hydroponic gardening at home.
- Bright Agrotech: This channel provides educational videos on hydroponics and vertical farming.
- Khang Starr: He shares his hydroponic pepper and tomato growing adventures.
Remember, while it’s great to learn from a variety of resources, nothing beats hands-on experience. Start your hydroponics journey, experiment, and learn as you grow.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydroponic gardening is an innovative and rewarding method of growing plants that offers numerous benefits such as faster growth rates, higher yields, less space requirement, and year-round cultivation. With the right knowledge and equipment, anyone can start their own hydroponic garden, whether you’re a city dweller with limited space or someone with a large backyard.
Our step-by-step guide covered the basics of hydroponics, including understanding what hydroponics is, selecting the right system, choosing and managing nutrients, regular maintenance, overcoming common challenges, and tips for success. We discussed essential supplies and equipment you’ll need to set up your hydroponic system and shared valuable resources for continuous learning and interaction with fellow hydroponic gardeners.
Remember, as with any new skill, starting small and gradually expanding your system as you gain more confidence and experience can be a fruitful approach. Hydroponic gardening is a blend of science and art; it allows you to experiment and learn as you grow.
Embrace the journey and don’t be discouraged by initial challenges or setbacks. With patience, persistence, and continuous learning, you’ll soon find yourself enjoying fresh, home-grown produce, contributing to a sustainable lifestyle, and potentially inspiring others to join the world of hydroponics.
Welcome to the fulfilling world of hydroponic gardening. Happy growing!






