
Aquaponics is a sustainable farming method that combines aquaculture (raising fish) and hydroponics (growing plants in water). There are several different types of aquaponic systems, each with its own unique characteristics and benefits. In this guide, we will explore the various types of aquaponic systems, including media-based, nutrient film technique, and more, and delve into how they work to create a symbiotic relationship between fish and plants.
Media-Based Aquaponic Systems
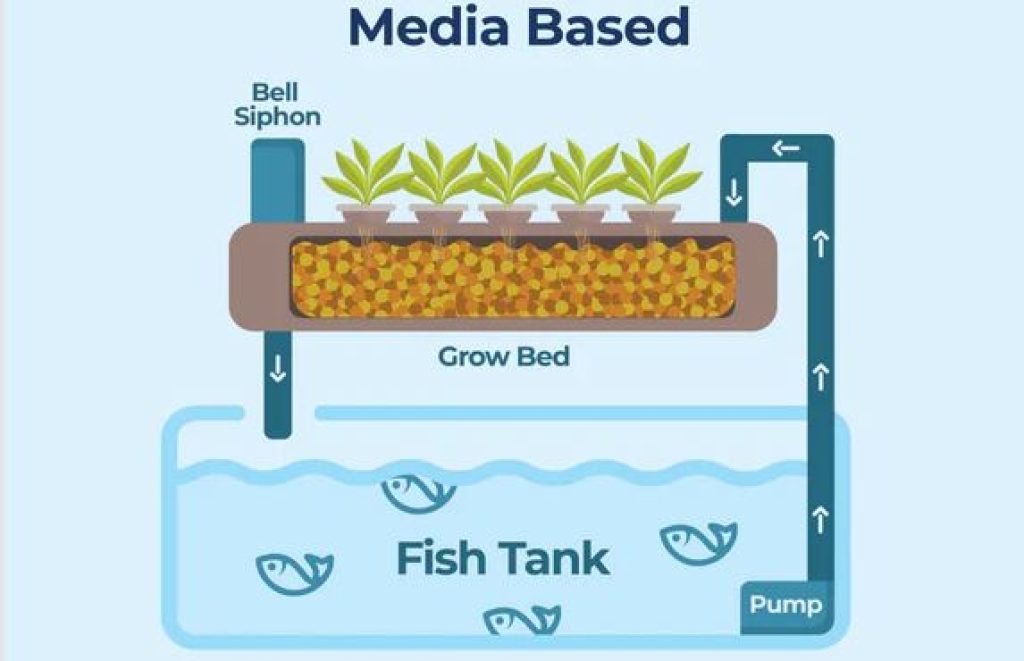
Media-based aquaponic systems are one of the most common types of aquaponic systems used by both hobbyists and commercial growers. In this system, plants are grown in a medium such as gravel, clay pellets, or coconut coir, which provides support for the plants and helps with nutrient absorption. The fish waste, which contains ammonia, is converted into nitrites and then nitrates by beneficial bacteria in the system. These nitrates are then taken up by the plants as a nutrient source, helping them to grow and thrive. The media also acts as a biofilter, providing a surface area for the beneficial bacteria to colonize and further break down the fish waste. Media-based aquaponic systems are versatile and can be used to grow a wide variety of plants, making them a popular choice for many aquaponic enthusiasts.
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) Aquaponic Systems
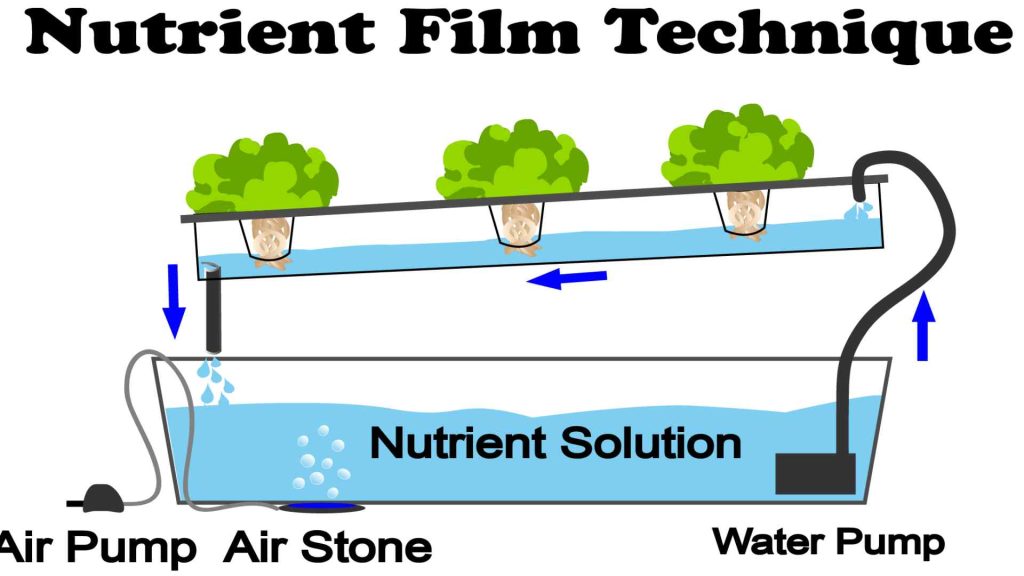
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT) aquaponic systems are another type of aquaponic system commonly used by growers. In this system, a thin film of nutrient-rich water flows continuously over the roots of the plants, providing them with a constant supply of nutrients. The water is then recirculated back to the fish tank, where it is filtered and oxygenated before being pumped back to the plants. NFT systems are known for their efficiency and water-saving capabilities, as they require less water compared to other systems. They are particularly suitable for growing leafy greens and herbs, as the constant flow of water helps to prevent root rot and provides optimal nutrient uptake for the plants. However, it’s important to monitor the flow rate and nutrient levels in NFT systems to ensure the plants receive the right amount of nutrients and water for healthy growth.
Deep Water Culture (DWC) Aquaponic Systems
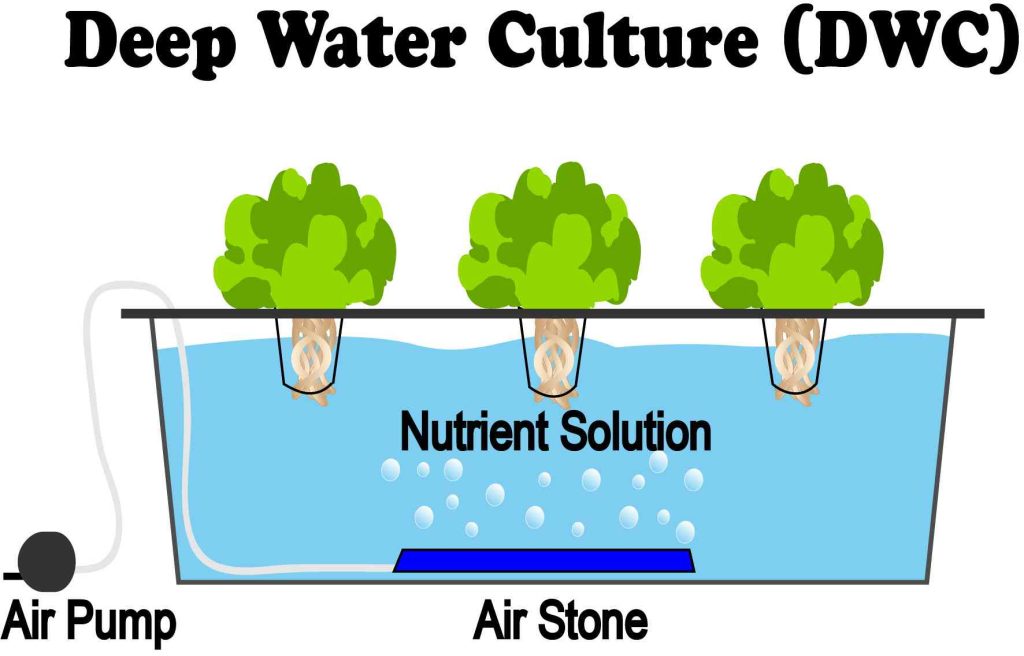
Deep Water Culture (DWC) aquaponic systems are a popular choice among aquaponic enthusiasts. In this system, the plants are suspended in a floating raft or net pots, with their roots submerged in nutrient-rich water. The water is continuously oxygenated using air stones or diffusers, providing the plants with a constant supply of oxygen. The fish waste in the water provides the necessary nutrients for the plants to grow. DWC systems are known for their simplicity and ease of use, making them suitable for beginners in aquaponics. They are particularly effective for growing larger plants with extensive root systems, such as tomatoes or cucumbers. However, it’s important to monitor the water temperature and oxygen levels in DWC systems to ensure optimal plant growth and fish health.
Vertical Aquaponic Systems
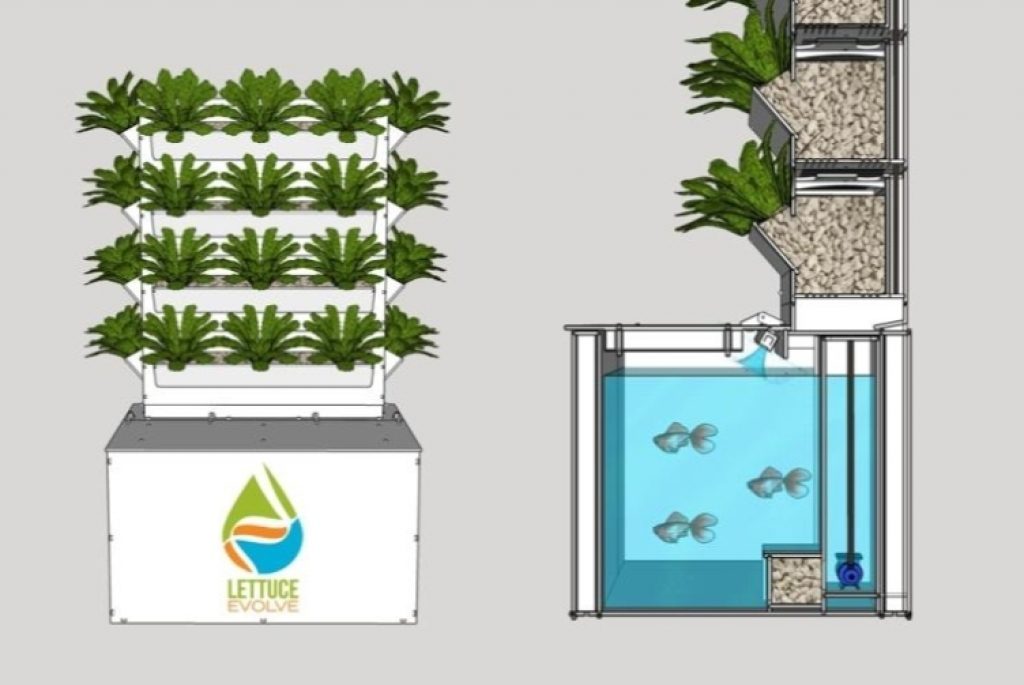

Vertical aquaponic systems are a unique and space-saving option for growing plants and raising fish. In these systems, the plants are stacked vertically, allowing for maximum use of space. The water from the fish tank is pumped up to the top of the system and then flows down through the different layers, providing nutrients to the plants. As the water trickles down, it is filtered and purified, returning to the fish tank clean and oxygenated. This type of system is ideal for small spaces or urban environments where horizontal space is limited. It also allows for easy harvesting and maintenance, as the plants are at a convenient height. However, it’s important to ensure proper lighting and irrigation in vertical aquaponic systems to promote healthy plant growth.
Hybrid Aquaponic Systems
Hybrid aquaponic systems combine different types of aquaponic systems to maximize efficiency and productivity. These systems often incorporate elements of both media-based and nutrient film technique systems. For example, a hybrid system may use a media bed for growing larger plants, such as tomatoes or cucumbers, while also utilizing a nutrient film technique for growing smaller, leafy greens. This combination allows for a diverse range of crops to be grown in the same system, maximizing the use of space and resources. Hybrid systems can be more complex to set up and maintain, but they offer greater flexibility and potential for higher yields.
Choosing Your Aquaponic System: A Considered Decision
Choosing the right aquaponic system requires careful consideration of several factors, such as the type of plants you wish to grow, the space available, your budget, and the complexity of the system you’re comfortable handling. Each system has its unique set of pros and cons, so consider your individual circumstances and goals before making a decision.
Conclusion
Aquaponics offers a green thumb’s dream, combining sustainable fish farming with the joy of hydroponics. Whether you’re a beginner wanting to dip your toes in the water or a seasoned farmer looking to switch to a more sustainable approach, understanding the different types of aquaponic systems is the first step in your journey towards sustainable farming. Explore, experiment, and let your aquaponic adventure begin!






