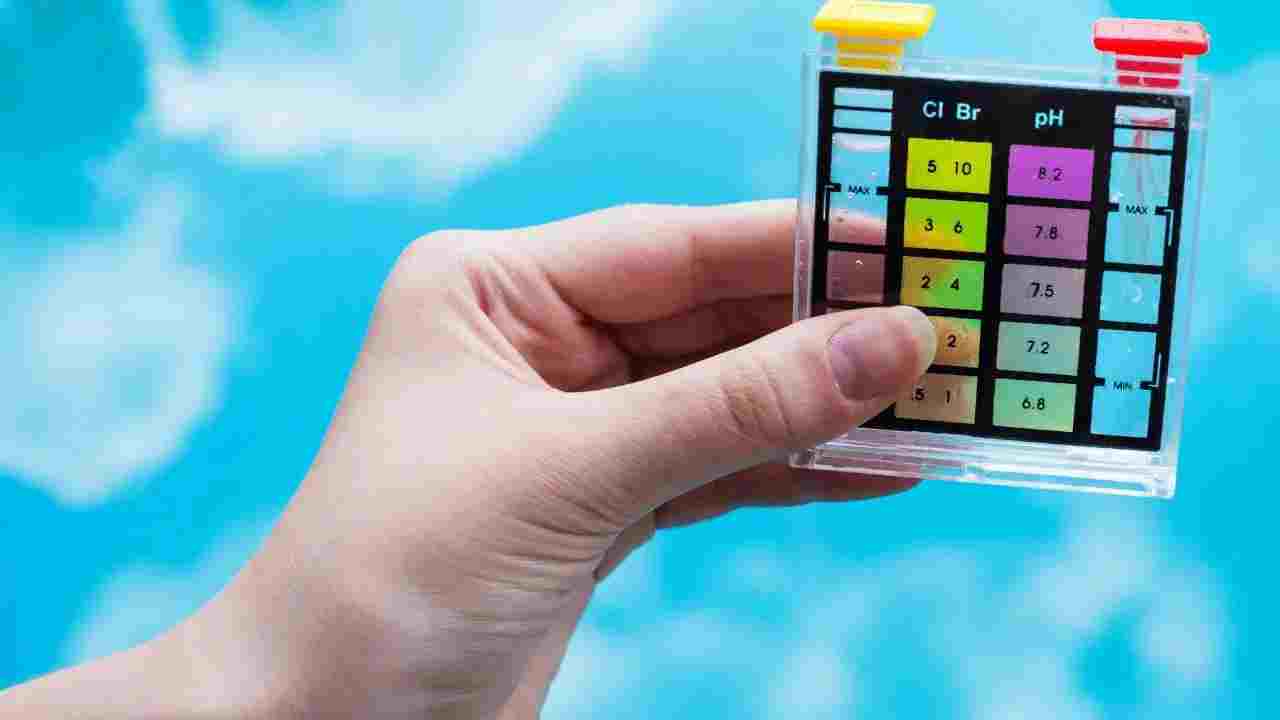
Are you ready to take your hydroponic gardening skills to the next level? If so, mastering pH levels is an essential step towards achieving optimal plant growth and maximizing your yields. In the world of hydroponics, pH refers to the acidity or alkalinity of the nutrient solution that your plants rely on for their growth. Maintaining the correct pH range is crucial for nutrient absorption and overall plant health. In this guide, we will explore the key tips and best practices for mastering hydroponic pH levels. We will delve into the importance of pH monitoring, the ideal pH range for different types of plants, and effective strategies for adjusting pH levels. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced hydroponic gardener, understanding and controlling pH is a skill that can significantly improve your gardening success. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets to mastering hydroponic pH levels!
Read more about: Nutrient for Hydroponics: The Ultimate Guide
Understanding pH levels in hydroponics
In hydroponic gardening, pH is a measurement of the acidity or alkalinity of the nutrient solution. It is measured on a scale from 0 to 14, with 7 being considered neutral. A pH below 7 indicates acidity, while a pH above 7 indicates alkalinity. For optimal plant growth, it is crucial to maintain the pH level within a specific range that suits the needs of the plants you are growing. Understanding the basics of pH levels in hydroponics is the first step towards mastering this important aspect of plant cultivation.

Maintaining the correct pH level is indeed crucial for successful plant growth in hydroponic systems. Let’s delve further into the significance of pH levels and its impact on plant health:
1. pH and Nutrient Availability: The pH level of the nutrient solution directly affects the availability of essential nutrients to plants. Each nutrient has an optimal pH range at which it is most readily available for uptake by plant roots. If the pH strays too far from this range, nutrient uptake can be hindered, even if the nutrients are present in the solution. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies and negatively impact plant health.
2. pH and Plant Physiology: pH influences various physiological processes in plants, such as enzyme activity and photosynthesis. These processes are sensitive to changes in pH, and maintaining the correct pH range ensures that these vital functions can occur efficiently.
3. pH Range for Hydroponics: The ideal pH range for hydroponic systems typically falls between 5.5 to 6.5. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral environment. However, some plants may have more specific pH preferences, and it’s essential to research the specific needs of the plants you are growing.
4. pH Monitoring and Adjustment: Regular monitoring of the pH level is essential to prevent pH drift. Factors like nutrient uptake, evaporation, and chemical reactions within the nutrient solution can cause pH fluctuations. pH should be checked using a pH meter or pH test kit and adjusted as needed.
5. pH Adjustment Solutions: pH can be adjusted using pH up (alkaline) or pH down (acidic) solutions. Common pH up solutions include potassium hydroxide, while pH down solutions typically contain phosphoric acid or nitric acid. When adjusting pH, it’s essential to make gradual changes and recheck the pH until the desired level is achieved.
6. pH and Hydroponic Systems: Different hydroponic systems may have varying pH maintenance requirements. For example, recirculating systems may require more frequent pH monitoring and adjustments due to potential nutrient build-up, while non-recirculating systems may have more stable pH levels.
Understanding pH levels and the importance of maintaining the correct pH range in hydroponics is crucial for providing the best environment for plant growth. With proper pH management, hydroponic gardeners can optimize nutrient uptake, promote healthy plant development, and ultimately achieve successful and productive hydroponic gardening.
The importance of maintaining proper pH levels in hydroponics
Maintaining proper pH levels in hydroponics is of utmost importance for several reasons. Firstly, pH levels directly affect nutrient availability. When the pH is too high or too low, certain essential nutrients can become unavailable to the plants, leading to nutrient deficiencies and stunted growth. Secondly, pH levels also affect the solubility of minerals and the overall health of the root system. If the pH is too high or too low, it can cause damage to the roots, leading to poor nutrient absorption and increased susceptibility to diseases. Finally, maintaining the correct pH range ensures optimal enzymatic activity in the plants, promoting healthy growth and higher yields. By understanding and maintaining proper pH levels, you can provide the best growing conditions for your hydroponic plants.
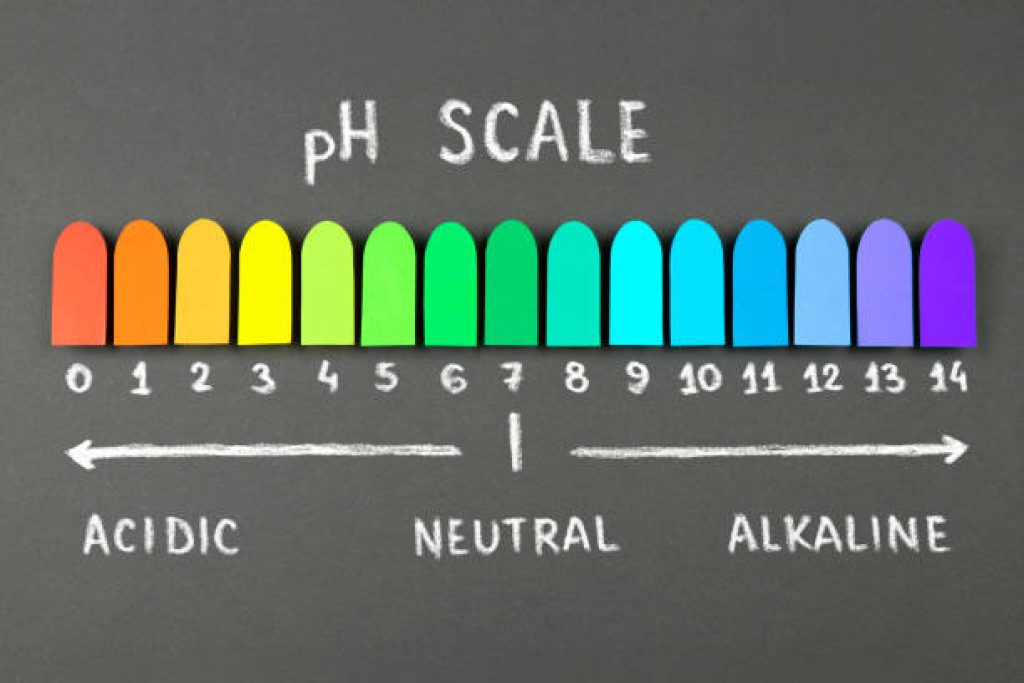
Let’s further explore the key reasons why pH management is crucial in hydroponics:
1. Nutrient Availability: pH levels directly impact nutrient availability in the nutrient solution. When the pH deviates from the optimal range, certain essential nutrients may become chemically bound and unavailable to plants. This can lead to nutrient deficiencies, even if the nutrients are present in the solution, and hinder plant growth and development.
2. Root Health and Nutrient Absorption: In hydroponics, the root system is directly exposed to the nutrient solution, and its health is vital for nutrient absorption. Proper pH levels promote a healthy root environment, enabling efficient nutrient uptake. Extreme pH levels can damage the delicate root structures, impair nutrient absorption, and create stress for the plants.
3. Mineral Solubility: pH affects the solubility of minerals in the nutrient solution. If the pH is too high or too low, certain minerals may precipitate out of the solution, forming insoluble compounds. This reduces the availability of those minerals to the plants and can lead to deficiencies.
4. Enzymatic Activity: Enzymes, which are essential for various biochemical reactions in plants, are highly sensitive to pH levels. Correct pH conditions support optimal enzymatic activity, facilitating essential cellular processes like photosynthesis, respiration, and protein synthesis.
5. Disease Resistance: A balanced pH environment contributes to stronger and healthier plants, making them more resistant to diseases and pests. Unfavorable pH levels can weaken the plant’s defense mechanisms, making them more susceptible to infections.
6. Consistent Growth and High Yields: By maintaining proper pH levels, hydroponic gardeners can provide the most favorable growing conditions for their plants. This consistency in the nutrient solution’s pH promotes stable plant growth and development, leading to higher yields and improved crop quality.
7. pH Management: Regular monitoring of pH levels and making necessary adjustments are essential to maintaining optimal pH conditions. pH fluctuations can occur due to various factors, such as nutrient uptake, evaporation, and nutrient solution changes. Gardeners must respond promptly to any pH deviations to ensure plant health.
By understanding the significance of maintaining proper pH levels in hydroponics and actively managing pH, hydroponic gardeners can create the best possible environment for their plants to thrive. This proactive approach contributes to healthier, more robust plants, resulting in successful and productive hydroponic gardening.
The ideal pH range for different hydroponic crops
Different hydroponic crops have varying pH requirements. While most plants thrive within a slightly acidic to slightly alkaline range, it is important to research and understand the specific pH preferences of the crops you are growing. Generally, the ideal pH range for most hydroponic crops falls between 5.5 and 6.5. However, some plants, such as strawberries and blueberries, prefer a more acidic environment, with a pH range of 4.5 to 5.5. On the other hand, lettuce and herbs tend to prefer a slightly more alkaline pH range of 6.0 to 6.5. It is essential to tailor the pH levels to the specific needs of your crops to ensure optimal growth and productivity.
Let’s delve further into the pH preferences of some common hydroponic crops:
1. General Ideal pH Range (for Most Crops): For the majority of hydroponic crops, a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5 is considered ideal. This slightly acidic to slightly alkaline range provides a suitable environment for nutrient availability and uptake, promoting healthy plant growth.
2. Acid-Loving Crops: Some crops prefer a more acidic environment. Examples of acid-loving crops include:
- Strawberries: Prefer a pH range of 5.5 to 6.5.
- Blueberries: Prefer a pH range of 4.5 to 5.5.
3. Alkaline-Loving Crops: While fewer hydroponic crops have a preference for alkaline conditions, some still prefer a slightly more alkaline pH range. Examples of alkaline-loving crops include:
- Lettuce: Prefer a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5.
- Herbs (e.g., Basil, Mint, Parsley): Prefer a pH range of 6.0 to 6.5.
4. Researching Specific Crop pH Preferences: For other hydroponic crops, it’s essential to research and understand their specific pH preferences. Some crops have narrower pH preferences, and maintaining the pH within their preferred range is critical for their growth and productivity.
5. Monitoring and Adjusting pH: Regular monitoring of pH levels and making necessary adjustments are vital for meeting the pH preferences of your crops. pH levels can fluctuate due to various factors, and it’s essential to maintain the pH within the desired range to avoid nutrient availability issues and potential plant stress.
6. Crop-Specific pH Charts: Some hydroponic resources provide crop-specific pH charts, detailing the recommended pH ranges for different plants. Consulting such charts can be beneficial for customizing the pH levels in your hydroponic system to match the needs of your crops.
By tailoring the pH levels to the specific preferences of your hydroponic crops, you can provide the most favorable conditions for their growth and development. This attention to pH management contributes to healthier, more resilient plants and ultimately leads to successful and rewarding hydroponic gardening with abundant harvests.
Testing and monitoring pH levels in hydroponics
Regular testing and monitoring of pH levels are crucial to maintaining optimal conditions for your hydroponic plants. There are several methods available for testing pH levels in hydroponics. One of the most common methods is using a pH meter or pH test kit. These tools allow you to accurately measure the pH of your nutrient solution and make necessary adjustments. Another method is using pH indicator solutions, which change color depending on the pH level. By comparing the color of the solution to a color chart, you can determine the pH level of your nutrient solution. Whichever method you choose, it is important to test and monitor pH levels regularly, as fluctuations can occur over time.
Let’s delve deeper into the importance of testing pH levels and the methods available for doing so:
1. Importance of pH Testing: pH directly affects nutrient availability and plant health. Monitoring pH allows you to ensure that essential nutrients are readily available to the plants and that the root environment remains conducive to nutrient uptake. Regular pH testing helps prevent nutrient deficiencies or toxicities that can arise from pH imbalances.
2. pH Testing Methods: There are several methods available for testing pH levels in hydroponics:
- pH Meter: A pH meter is a precise and commonly used tool for pH testing. It provides accurate pH readings, allowing you to monitor small changes in pH levels. pH meters come in various types, including handheld, portable, and benchtop models.
- pH Test Kit: A pH test kit is an affordable and straightforward option for pH testing. It usually includes pH indicator solutions and a color chart. By adding a few drops of the indicator solution to a sample of the nutrient solution and comparing the resulting color to the chart, you can determine the pH level.
- pH Indicator Strips: pH indicator strips are similar to pH test kits but come in the form of paper strips with a pH-sensitive coating. Dip the strip into the nutrient solution, and it will change color to indicate the pH level.
3. Frequency of pH Monitoring: The frequency of pH monitoring depends on various factors, including the specific hydroponic system, plant types, and nutrient solution characteristics. As a general guideline, pH should be tested at least once a day in most hydroponic systems. For more stable systems or if you’re experienced with your specific setup, you may test pH less frequently but still regularly to ensure pH remains within the desired range.
4. pH Adjustment: If the pH level deviates from the optimal range, adjustments are necessary to bring it back within the desired parameters. pH up or pH down solutions can be used to raise or lower pH levels, respectively. When making adjustments, do so gradually and retest until the desired pH level is achieved.
5. Record Keeping: Maintaining a record of pH measurements, adjustments made, and any changes in plant health can provide valuable insights into the performance of your hydroponic system. This record-keeping can help you fine-tune your nutrient management over time.
By regularly testing and monitoring pH levels in your hydroponic system, you can ensure that your plants have access to the optimal pH conditions for nutrient uptake and overall health. This proactive approach to pH management contributes to successful and productive hydroponic gardening.
Adjusting pH levels in hydroponics
Once you have tested the pH levels of your hydroponic system, you may need to make adjustments to bring them within the desired range. There are several methods for adjusting pH levels in hydroponics. One common method is using pH up and pH down solutions. pH up solutions are used to raise the pH, while pH down solutions are used to lower the pH. These solutions contain chemicals that help neutralize the acidity or alkalinity of the nutrient solution. Another method is using natural pH adjusters, such as vinegar or lemon juice, to lower the pH, or baking soda to raise the pH. It is important to make gradual adjustments to avoid drastic pH swings, as this can shock the plants. Regular monitoring and adjustment of pH levels will ensure that your plants are receiving the optimal nutrient uptake.
Common pH problems in hydroponics and how to troubleshoot them
In hydroponics, there are a few common pH problems that can arise. One common issue is pH drift, which occurs when the pH level gradually changes over time. This can be caused by factors such as nutrient uptake by the plants or the accumulation of salts in the nutrient solution. To troubleshoot pH drift, it is important to regularly test and adjust pH levels to maintain a stable range. Another common problem is pH lockout, which occurs when the pH level is outside the optimal range, leading to nutrient deficiencies. To troubleshoot pH lockout, it is important to adjust the pH to the correct range and ensure that the plants are receiving the necessary nutrients. By understanding and troubleshooting common pH problems, you can ensure that your hydroponic system is operating at its best.
Let’s delve further into these issues and discuss how to troubleshoot them effectively:
1. pH Drift: Causes: pH drift occurs when the pH level gradually changes over time. Factors that can lead to pH drift include nutrient uptake by the plants, microbial activity, evaporation, and the accumulation of dissolved solids (salts) in the nutrient solution.
Troubleshooting: To troubleshoot pH drift:
- Regular Testing: Test the pH of your nutrient solution regularly, preferably daily, to identify any changes in pH levels over time.
- Adjustment: When you detect a drift, use pH up or pH down solutions to bring the pH back to the desired range. Make gradual adjustments and retest until the correct pH is achieved.
- Monitor Nutrient Levels: Excessive nutrient buildup can contribute to pH drift. Monitor the nutrient concentration in your solution and perform regular solution changes to prevent excessive accumulation of dissolved solids.
- Maintain Proper Aeration: Adequate aeration can help prevent pH drift caused by microbial activity. Proper oxygenation in the nutrient solution discourages anaerobic conditions that may alter pH levels.
2. pH Lockout: Causes: pH lockout occurs when the pH level of the nutrient solution falls outside the optimal range for nutrient uptake by the plants. This can lead to certain nutrients becoming less available to the plants, resulting in nutrient deficiencies.
Troubleshooting: To troubleshoot pH lockout:
- pH Adjustment: Test the pH and adjust it to the optimal range for your specific crops (usually between 5.5 to 6.5 for most plants). This will ensure that nutrients remain available for uptake.
- Nutrient Balance: Check the nutrient composition in your solution. If you identify specific nutrient deficiencies, adjust the nutrient solution to supply the missing elements in the right proportions.
- Inspect Root Health: pH lockout can sometimes be caused by root-related issues. Ensure that the root system is healthy, free from diseases, and well-aerated.
- Monitor Water Quality: Water quality can affect pH levels. Ensure that the water used for the nutrient solution is of good quality, and consider using a water filter if necessary.
- Avoid Overfeeding: Over-fertilization can lead to pH imbalances and nutrient lockout. Follow the recommended nutrient dosages and avoid excessive nutrient concentrations.
By understanding and effectively troubleshooting common pH problems in hydroponics, you can maintain a stable and optimal pH environment for your plants. Regular testing, monitoring, and adjustments are essential for ensuring that your hydroponic system operates at its best, promoting healthy plant growth and maximizing crop yields.
Best practices for maintaining optimal pH levels in hydroponics
To maintain optimal pH levels in hydroponics, there are several best practices to keep in mind. Firstly, it is important to test and monitor pH levels regularly to catch any fluctuations early on. Secondly, it is recommended to make gradual adjustments to pH levels to avoid shocking the plants. Additionally, it is important to maintain a clean and well-maintained hydroponic system, as factors such as algae growth or clogged irrigation systems can impact pH levels. Lastly, it is crucial to provide the correct nutrient balance and ensure that the plants are receiving all the necessary elements for healthy growth. By following these best practices, you can create the ideal growing environment for your hydroponic plants.
Let’s summarize these best practices:
1. Regular pH Testing and Monitoring: Regularly test the pH of the nutrient solution, preferably on a daily basis or as needed, to catch any fluctuations in pH levels early on. pH can change over time due to various factors, and regular monitoring helps to identify and address any deviations promptly.
2. Gradual pH Adjustments: When adjusting pH levels, make changes gradually. This approach prevents sudden shifts in pH, which could shock the plants and cause stress. Gradual adjustments also allow for better control and minimize the risk of overcorrection.
3. Maintain a Clean Hydroponic System: Ensure that your hydroponic system is clean and well-maintained. Algae growth or debris accumulation can affect pH levels and nutrient solution quality. Regularly clean and sanitize your hydroponic equipment to prevent potential issues.
4. Address Root Zone Issues: Inspect and maintain the health of the root system. Healthy roots are essential for efficient nutrient uptake and help maintain a stable pH environment. Avoid root rot or other root-related issues that could impact nutrient absorption.
5. Optimize Irrigation System: Ensure that your irrigation system is functioning correctly and efficiently. Clogged or malfunctioning irrigation components can disrupt nutrient distribution and affect pH levels.
6. Provide the Correct Nutrient Balance: Maintain a well-balanced nutrient solution tailored to the specific needs of your plants. Proper nutrient composition is vital for healthy plant growth and nutrient availability. Follow the recommended nutrient dosage and avoid over-fertilization.
7. Monitor Water Quality: Water quality can influence pH levels in the nutrient solution. Consider using filtered water, and if using tap water, be aware of its mineral content and pH. Adjust the water quality, if necessary, to create a more suitable nutrient solution.
8. Observe Plant Health and Growth: Regularly observe the health and growth of your hydroponic plants. Healthy plants are better equipped to handle pH fluctuations and stress. Address any signs of nutrient deficiencies or other issues promptly.
By following these best practices, hydroponic gardeners can maintain an optimal pH environment in their systems, promoting healthy and vigorous plant growth. A stable and well-balanced pH level ensures that essential nutrients are readily available for plant uptake, leading to successful and rewarding hydroponic gardening with abundant yields.
pH adjustment methods in hydroponics – organic vs. chemical
When it comes to adjusting pH levels in hydroponics, there are two main approaches: organic and chemical. Organic pH adjustment methods involve the use of natural substances, such as citric acid, vinegar, or baking soda, to raise or lower pH levels. These methods are often preferred by organic gardeners who want to avoid the use of synthetic chemicals. On the other hand, chemical pH adjustment methods involve the use of pH up and pH down solutions, which contain chemicals specifically designed to adjust pH levels. Both methods have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice between organic and chemical pH adjustment depends on personal preference and the specific needs of your plants.
Let’s further explore the characteristics, advantages, and considerations of each method:
Organic pH Adjustment: Characteristics: Organic pH adjustment involves the use of natural substances that can raise or lower the pH of the nutrient solution. Common organic pH adjusters include citric acid, vinegar (acetic acid), and baking soda (sodium bicarbonate).
Advantages:
- Organic pH adjusters are derived from natural sources, which may appeal to organic gardeners who prefer to avoid synthetic chemicals in their hydroponic systems.
- They can be readily available in households or easily sourced from natural stores.
- Organic pH adjusters can be less harsh on the plants and the environment compared to some chemical alternatives.
Considerations:
- Organic pH adjusters may not provide as precise or rapid pH adjustments as chemical solutions.
- The concentration and effectiveness of organic pH adjusters may vary, requiring careful measurement and experimentation.
- Some organic pH adjusters, like vinegar, can introduce additional substances (e.g., acetic acid) into the nutrient solution, which may have side effects on plant health or growth.
Chemical pH Adjustment: Characteristics: Chemical pH adjustment involves the use of pH up and pH down solutions specifically formulated to raise or lower pH levels in the nutrient solution. These solutions usually contain synthetic chemicals like phosphoric acid (pH down) or potassium hydroxide (pH up).
Advantages:
- Chemical pH adjusters offer precise and rapid pH adjustments, making it easier to maintain the desired pH range.
- They are widely available and formulated for hydroponic use, providing reliable and consistent results.
- pH up and pH down solutions are convenient to use, requiring minimal experimentation.
Considerations:
- Some chemical pH adjusters are synthetic, which may not align with the preferences of organic gardeners.
- Care should be taken when handling chemical solutions to avoid skin or eye contact and inhalation of fumes. Use them in a well-ventilated area and wear appropriate protective gear.
Choosing Between Organic and Chemical pH Adjustment: The choice between organic and chemical pH adjustment depends on personal preference, gardening philosophy, and the specific needs of your plants. Organic gardeners may prefer using natural substances despite the potential challenges in precision and effectiveness. On the other hand, those seeking convenience and precision may opt for chemical pH adjusters, even if they are not strictly organic.
Whichever method is chosen, it is essential to monitor pH levels regularly and make adjustments as needed to maintain the optimal pH range for your hydroponic plants. Proper pH management is crucial for ensuring nutrient availability, plant health, and successful hydroponic gardening.
Tools and equipment for pH management in hydroponics
To effectively manage pH levels in hydroponics, there are several tools and equipment that can assist you. The most common tool is a pH meter or pH test kit, which allows you to accurately measure the pH level of your nutrient solution. pH buffer solutions are also useful for calibrating your pH meter and ensuring accurate readings. Additionally, pH up and pH down solutions are essential for making adjustments to pH levels. It is also recommended to have a backup pH meter or test kit to ensure accurate readings and avoid any downtime in pH monitoring. By having the right tools and equipment, you can successfully manage and maintain optimal pH levels in your hydroponic system.
Let’s summarize the key tools and equipment:
1. pH Meter or pH Test Kit: A pH meter or pH test kit is a primary tool for measuring the pH level of your nutrient solution. pH meters provide precise digital readings, while pH test kits use color indicators to estimate pH levels based on color changes.
2. pH Buffer Solutions: pH buffer solutions are essential for calibrating your pH meter regularly. They provide reference points at specific pH values (e.g., pH 4.0, pH 7.0, and pH 10.0) to ensure the accuracy of your pH meter readings.
3. pH up and pH down Solutions: pH up and pH down solutions are used to adjust the pH level of the nutrient solution. pH up (alkaline) solutions are used to raise the pH, while pH down (acidic) solutions are used to lower the pH.
4. Backup pH Meter or Test Kit: Having a backup pH meter or test kit is recommended as a contingency measure. In case your primary pH meter malfunctions or requires calibration, having a backup ensures you can continue monitoring pH levels without interruptions.
5. Storage Solution for pH Meter: If you’re using a pH meter, it’s essential to store the electrode properly when not in use. A pH storage solution helps keep the electrode hydrated and maintains its accuracy.
6. Calibration and Maintenance Tools: Ensure you have the necessary tools for calibrating and maintaining your pH meter, such as a small brush for cleaning the electrode and storage solutions for long-term electrode maintenance.
7. pH Data Loggers (Optional): For more advanced monitoring, pH data loggers can automatically record pH readings at specified intervals, providing valuable data for analysis and trend tracking.
8. Protective Gear (Gloves, Goggles): When handling pH up and pH down solutions, it’s essential to protect yourself by wearing gloves and safety goggles to avoid any potential skin or eye contact.
Having the right tools and equipment for pH management is crucial for maintaining optimal pH levels in your hydroponic system. Regular testing, adjustments, and proper calibration help ensure that your plants have the best possible growing environment, leading to healthy and productive hydroponic gardening.
Conclusion: Achieving success with hydroponic pH levels
Mastering pH levels in hydroponics is an essential skill for any hydroponic gardener. By understanding the importance of pH levels, testing and monitoring regularly, and making necessary adjustments, you can provide the best growing conditions for your hydroponic plants. Remember to tailor the pH levels to the specific needs of your crops and troubleshoot any pH problems that may arise. Whether you choose organic or chemical pH adjustment methods, the key is to maintain a stable pH range that promotes nutrient absorption and overall plant health. With these key tips and best practices, you can achieve success in mastering hydroponic pH levels and take your gardening skills to new heights!
Remember that pH management is an ongoing process and requires regular attention. As you gain experience and fine-tune your pH management skills, you’ll be able to create a more stable and productive hydroponic system, leading to healthy and bountiful harvests.






