Welcome to the ultimate guide on nutrients for hydroponics! If you’re a hydroponic enthusiast or just getting started with this innovative gardening method, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything you need to know about selecting and using nutrients to cultivate healthy and thriving plants in your hydroponic system. From understanding the different types of nutrients and their roles in plant growth, to learning how to create a balanced nutrient solution tailored to your specific plants’ needs, we’ve got you covered. Whether you’re growing leafy greens, herbs, or even flowers and fruits, mastering the art of nutrient management is essential for maximizing your yields and achieving optimal plant health. With our step-by-step instructions, expert tips, and practical advice, you’ll be well-equipped to take your hydroponic gardening to new heights. So, let’s dive in and unlock the secrets of hydroponic nutrients together!
What are Nutrients in Hydroponics?
In traditional soil-based gardening, plants obtain nutrients from the soil. However, in hydroponics, where plants are grown without soil, nutrients are provided directly to the roots through a nutrient solution. These nutrients are essential for plant growth and development, as they serve as the building blocks for various cellular processes. By understanding the role of nutrients in hydroponics, you can ensure that your plants receive the necessary elements for their optimal growth and productivity.

In hydroponic systems, nutrients are dissolved in water to form a nutrient solution, which is then delivered directly to the plant roots. This way, plants receive the essential elements required for their growth and development without the need for soil.
The nutrients in hydroponic solutions are crucial for various cellular processes, such as photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and enzyme activation. Each nutrient plays a specific role in supporting plant health and function. Macronutrients like nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg), and sulfur (S) are required in relatively larger quantities. Micronutrients such as iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), boron (B), zinc (Zn), copper (Cu), molybdenum (Mo), chlorine (Cl), nickel (Ni), and silicon (Si) are needed in smaller amounts but are equally essential for plant growth.
By understanding the importance of nutrients in hydroponics and providing a well-balanced nutrient solution, hydroponic gardeners can ensure that their plants receive the optimal nutrition they need to thrive and produce healthy yields. Monitoring nutrient levels and making adjustments when necessary is essential for maintaining a healthy and productive hydroponic system.
The Importance of Nutrients in Hydroponics
Nutrients play a crucial role in hydroponic systems, where plants rely solely on the nutrient solution for their sustenance. In a soilless environment, it’s important to provide a well-balanced nutrient solution to mimic the conditions that plants would typically experience in the ground. The right nutrients in the correct proportions are necessary for healthy plant growth, strong root development, and the production of abundant and high-quality crops. Neglecting nutrient requirements can lead to nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, stunting plant growth and negatively impacting yields. Therefore, understanding the importance of nutrients and their specific roles in hydroponics is key to successful gardening.

The role of nutrients in hydroponics is multi-faceted:
- Supporting Plant Growth: Nutrients are the building blocks for various cellular processes, including photosynthesis, respiration, and protein synthesis. Adequate nutrient supply promotes healthy leafy growth, strong stems, and robust root development.
- Ensuring Nutrient Uptake: In hydroponics, nutrient uptake is a passive process driven by osmosis and diffusion. A properly balanced nutrient solution ensures that essential elements are available in the right concentrations for efficient uptake by plant roots.
- Optimizing Crop Yields: Providing the correct nutrients in the correct ratios throughout the growth stages helps maximize plant productivity and crop yields. Proper nutrient management can lead to larger and healthier harvests.
- Preventing Nutrient Deficiencies and Toxicities: Maintaining a well-balanced nutrient solution helps prevent nutrient deficiencies, which can cause yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and reduced fruiting. Additionally, it avoids nutrient toxicities, which can negatively impact plant health and development.
- Promoting Plant Health and Resistance: An optimal nutrient supply contributes to plant vigor and stress resistance, making plants less susceptible to diseases and environmental challenges.
- Customizing Nutrient Solutions: Different plant species and growth stages have varying nutrient requirements. By understanding the specific nutrient needs of your plants, you can adjust the nutrient solution to match their preferences, ensuring their optimal development.
Understanding the specific roles of nutrients and their importance in hydroponics allows growers to provide the best possible conditions for plant growth and productivity. Regular monitoring, observation, and nutrient solution adjustments are key to maintaining a healthy and thriving hydroponic system. With proper nutrient management, hydroponic gardeners can achieve impressive results, growing vigorous, lush plants and enjoying a bountiful harvest.
Essential Nutrients for Hydroponic Plants
Just like humans, plants require a variety of nutrients to thrive. However, plants have different nutrient requirements compared to humans. There are 16 essential nutrients that plants need for their growth and development. These nutrients are divided into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients. While macronutrients are required in larger quantities, micronutrients are needed in smaller amounts. Understanding the importance of each nutrient and how to provide them in the correct ratios is essential for maintaining the health and productivity of your hydroponic plants.
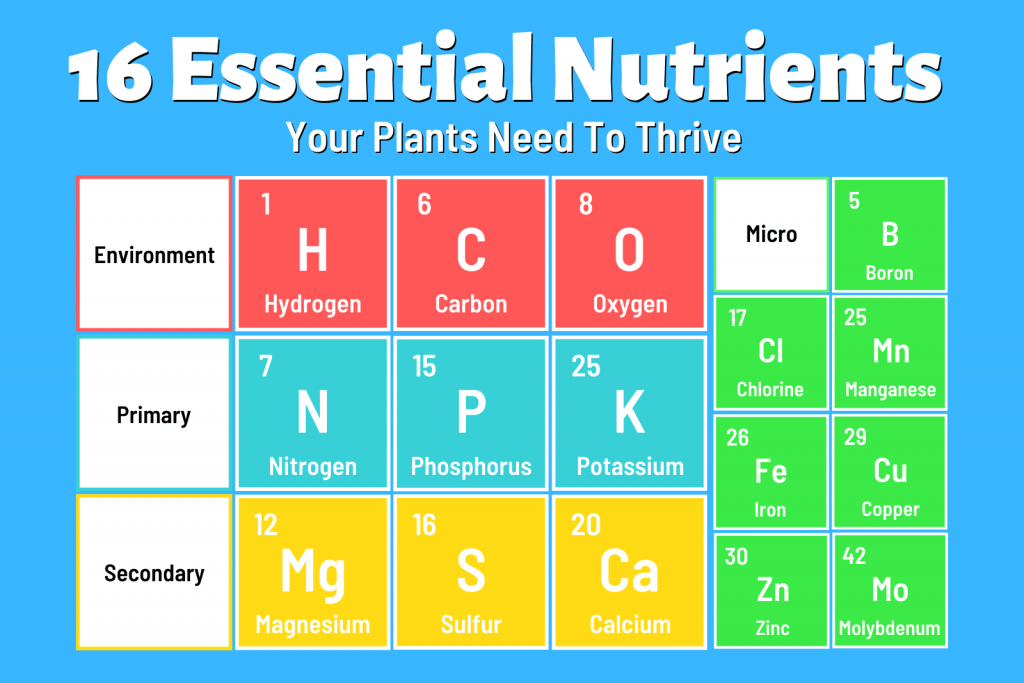
Macronutrients for Hydroponics
Macronutrients are the primary nutrients that plants need in larger quantities.
They include:
- Nitrogen (N): Essential for leafy green growth and the formation of proteins, enzymes, and chlorophyll.
- Phosphorus (P): Important for root development, flowering, fruiting, and energy transfer within the plant.
- Potassium (K): Aids in overall plant health, water uptake, enzyme activation, and stress tolerance.
- Calcium (Ca): Vital for cell wall structure, root development, and nutrient uptake.
- Magnesium (Mg): A component of chlorophyll, necessary for photosynthesis and overall plant energy production.
- Sulfur (S): Essential for the formation of certain amino acids and proteins in plants.
Each macronutrient plays a significant role in plant development. Nitrogen is essential for leaf and stem growth, phosphorus promotes root development and flowering, potassium aids in overall plant health and disease resistance, calcium strengthens cell walls, magnesium is vital for chlorophyll production, and sulfur is involved in protein synthesis. Providing these macronutrients in the right amounts is crucial for promoting healthy growth and maximizing yields.
Micronutrients for Hydroponics
In addition to macronutrients, plants require micronutrients, also known as trace elements, in smaller quantities.
These include:
- Iron (Fe): Important for chlorophyll production and various enzymatic processes within the plant.
- Manganese (Mn): Involved in chlorophyll synthesis and antioxidant defense systems.
- Boron (B): Required for cell division, pollination, and carbohydrate metabolism.
- Zinc (Zn): Aids in the synthesis of proteins and growth hormones, as well as enzyme activation.
- Copper (Cu): Necessary for photosynthesis and enzyme functioning.
- Molybdenum (Mo): Facilitates the conversion of nitrogen into a usable form by plants.
- Chlorine (Cl): Involved in water and nutrient movement within the plant.
- Nickel (Ni): Plays a role in nitrogen metabolism in certain plants.
- Sodium (Na): While not always considered essential, some plants may benefit from low levels of sodium.
- Silicon (Si): Some consider silicon as beneficial for plant health, helping with structural strength and resistance to pests and diseases.
Although they are needed in smaller amounts, micronutrients are equally important for plant growth and development. They are involved in various metabolic processes, enzyme activation, and the synthesis of essential molecules. Providing micronutrients in the correct ratios ensures that plants have access to these vital elements for their optimal functioning.
Organic vs. Synthetic Nutrients in Hydroponics
When it comes to hydroponic nutrients, you have the option to choose between organic and synthetic sources. Organic nutrients are derived from natural sources, such as compost, manure, or plant-based materials. They provide a slow-release form of nutrients, as they need to be broken down by microorganisms before plants can utilize them. On the other hand, synthetic nutrients are chemically formulated and readily available for plant uptake. They provide a quick and easily accessible source of nutrients. Both organic and synthetic nutrients have their advantages and disadvantages, and the choice ultimately depends on personal preference, environmental considerations, and the specific needs of your plants.
Let’s delve into more detail about their advantages and disadvantages:
Organic Nutrients:
Advantages:
- Natural and Sustainable: Organic nutrients are derived from renewable sources, making them more environmentally friendly.
- Slow-Release: They provide a gradual and steady supply of nutrients as they are broken down by microorganisms, reducing the risk of over-fertilization.
- Beneficial Microorganisms: Organic nutrients promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms in the root zone, contributing to a healthier root environment.
- Enhanced Soil Structure: In some hydroponic systems that use organic substrates like coconut coir or peat moss, organic nutrients can improve the overall structure and water-holding capacity of the medium.
Disadvantages:
- Potential Contamination: Organic nutrients can sometimes carry pathogens or unwanted organisms, leading to plant diseases or pest issues.
- Inconsistent Composition: The nutrient content of organic sources can vary, making it challenging to maintain precise nutrient ratios.
- Clogging: Some organic nutrients might clog hydroponic system components like pumps or filters.
- Slower Uptake: Plants may not have immediate access to nutrients, as they rely on microbial breakdown first.
Synthetic Nutrients:
Advantages:
- Precise Nutrient Control: Synthetic nutrients provide a consistent and precise nutrient composition, allowing for fine-tuning of nutrient solutions based on plant needs.
- Fast-Acting: Plants can access synthetic nutrients immediately, leading to rapid growth responses.
- Clean and Sterile: Synthetic nutrients are less likely to introduce pathogens or pests into the hydroponic system.
- Efficient Uptake: Plants can absorb synthetic nutrients more efficiently, as there are no intermediate steps required for breakdown.
Disadvantages:
- Environmental Concerns: The production of synthetic nutrients may have environmental impacts due to energy consumption and waste generation.
- Salt Buildup: Over time, synthetic nutrient use may lead to salt accumulation in the hydroponic system, requiring regular flushing to prevent issues.
- pH Imbalances: Synthetic nutrients can alter the pH of the nutrient solution more drastically, requiring careful pH monitoring and adjustment.
- Chemical Dependency: Some argue that prolonged use of synthetic nutrients may lead to dependency, reducing a plant’s ability to thrive without them.
Ultimately, the choice between organic and synthetic nutrients depends on the specific goals, preferences, and resources of the hydroponic gardener. Some growers may prefer the sustainability and potential long-term benefits of organic nutrients, while others may opt for the precision and immediate results provided by synthetic nutrients. In some cases, a combination of both organic and synthetic nutrient sources can be used to harness the advantages of each and mitigate their respective disadvantages.
Nutrient Deficiency and Toxicity in Hydroponics
While providing the right nutrients is essential, it’s equally important to avoid nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. Nutrient deficiencies occur when plants do not receive adequate amounts of a particular nutrient, leading to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, or other visible symptoms. On the other hand, nutrient toxicities occur when plants are exposed to excessive amounts of a nutrient, which can cause nutrient imbalances and adversely affect plant health. Monitoring your plants regularly, understanding the signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, and adjusting your nutrient solution accordingly is crucial for maintaining a healthy growing environment.
Monitoring and maintaining the right nutrient balance in the hydroponic solution is essential to prevent nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, which can significantly impact plant health and productivity. Let’s explore nutrient deficiencies and toxicities in more detail:
Nutrient Deficiencies: Nutrient deficiencies occur when plants do not receive sufficient amounts of specific essential nutrients. The symptoms of nutrient deficiencies can vary depending on the nutrient that is lacking, but some common signs include:
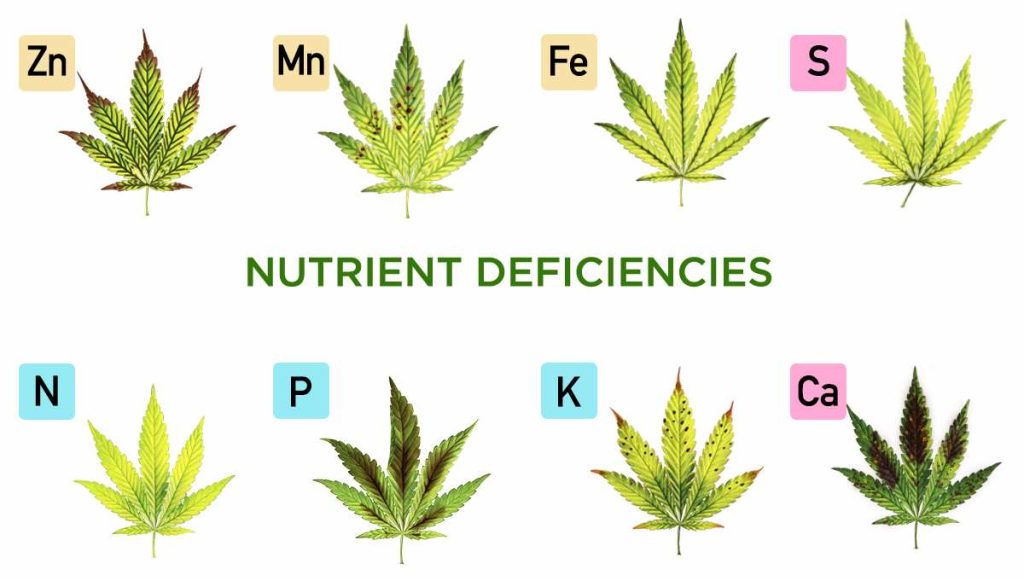
- Nitrogen (N) Deficiency: Yellowing of older leaves (chlorosis), starting from the tips and spreading inward, along with overall stunted growth.
- Phosphorus (P) Deficiency: Purplish or reddish discoloration of leaves, especially on the undersides, and poor root development.
- Potassium (K) Deficiency: Leaf margins turning yellow or brown, starting from older leaves, and weak, spindly stems.
- Calcium (Ca) Deficiency: Affected leaves may show yellowing between the veins (interveinal chlorosis), distorted growth, and increased susceptibility to diseases.
- Magnesium (Mg) Deficiency: Yellowing between leaf veins (interveinal chlorosis) on older leaves, while the veins themselves remain green.
- Sulfur (S) Deficiency: New leaves may appear pale or yellowish, and plant growth can be reduced.
- Micronutrient Deficiencies: Symptoms vary for different micronutrients, but they can include chlorosis, leaf curling, or abnormal growth patterns.
Nutrient Toxicities: Nutrient toxicities occur when plants are exposed to excessive amounts of certain nutrients. This imbalance can negatively affect nutrient uptake and lead to visible symptoms. Some signs of nutrient toxicities include:
- Nitrogen (N) Toxicity: Lush, dark green foliage, but reduced fruiting and flowering.
- Phosphorus (P) Toxicity: Rare in hydroponics but can cause micronutrient imbalances and stunted root growth.
- Potassium (K) Toxicity: Rare in hydroponics but may lead to calcium and magnesium imbalances.
- Micronutrient Toxicities: Each micronutrient may cause specific symptoms, but they generally include leaf discoloration and distorted growth.
Preventing and Addressing Imbalances: To prevent and address nutrient deficiencies or toxicities, it’s essential to regularly monitor the nutrient solution’s pH, electrical conductivity (EC), and nutrient levels. Conduct visual inspections of the plants for any signs of nutrient-related issues.
When a deficiency or toxicity is identified, adjustments to the nutrient solution can be made by either increasing the concentration of the deficient nutrient or diluting the entire solution to reduce toxic levels. pH adjustments may also be necessary to enhance nutrient uptake. Using high-quality nutrient formulations and adhering to the recommended guidelines for specific plant types can help maintain a balanced nutrient environment.
By staying vigilant and proactive in managing nutrient levels, hydroponic gardeners can ensure that their plants receive the optimal nutrition they need to thrive and produce healthy yields.
Choosing the Right Nutrient Solution for Your Hydroponic System
Selecting the right nutrient solution is a critical step in hydroponic gardening. It involves creating a well-balanced solution that meets the specific nutrient requirements of your plants. Factors such as plant type, growth stage, and water quality should be taken into consideration when formulating your nutrient solution. By understanding the nutrient needs of your plants and adjusting your solution accordingly, you can ensure that your plants receive the optimal nutrition they require for healthy growth and development.
Choosing the Right Nutrient Solution for Your Hydroponic System
Selecting the right nutrient solution is a critical step in hydroponic gardening. It involves creating a well-balanced solution that meets the specific nutrient requirements of your plants. Factors such as plant type, growth stage, and water quality should be taken into consideration when formulating your nutrient solution. By understanding the nutrient needs of your plants and adjusting your solution accordingly, you can ensure that your plants receive the optimal nutrition they require for healthy growth and development.

Absolutely right! Choosing the right nutrient solution is essential for successful hydroponic gardening. It involves creating a balanced and customized solution that meets the specific needs of your plants throughout their growth stages. Here are some important considerations when formulating your nutrient solution:
1. Plant Type and Growth Stage: Different plants have varying nutrient requirements at different stages of their growth. For example, leafy greens have higher nitrogen needs during vegetative growth, while flowering plants may require more phosphorus and potassium for bloom development. Research the specific nutrient needs of the plants you are growing and adjust the nutrient solution accordingly as they progress through their growth cycle.
2. Essential Nutrients: Ensure that your nutrient solution provides all the essential nutrients required for plant growth. As mentioned earlier, these include macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur) and micronutrients (iron, manganese, boron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, chlorine, nickel, and silicon). Commercial hydroponic nutrient solutions are usually formulated to include all these essential elements.
3. Water Quality: The quality of the water you use in your hydroponic system can affect nutrient availability and pH levels. Conduct a water test to determine its initial nutrient content and pH. Depending on your water source, you may need to adjust the nutrient solution to account for any existing mineral content or pH imbalances.
4. pH and EC Levels: Maintaining the correct pH and electrical conductivity (EC) levels in the nutrient solution is crucial. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range (typically between 5.5 to 6.5) for optimal nutrient uptake. EC levels indicate the concentration of dissolved nutrients in the solution and can be adjusted to match the specific needs of your plants.
5. Commercial vs. DIY Formulations: You can choose between commercially available pre-formulated nutrient solutions or create your own DIY nutrient solution by mixing individual nutrient salts. Commercial formulations are convenient and usually designed for specific plant types and growth stages. DIY solutions offer more flexibility, allowing you to fine-tune nutrient ratios, but they require a deeper understanding of nutrient chemistry.
6. Nutrient Solution Management: Monitor your plants regularly for any signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. As plants grow and environmental conditions change, nutrient uptake requirements may vary. Adjust the nutrient solution accordingly to maintain a healthy nutrient balance.
7. Consider Hydroponic System Type: The type of hydroponic system you are using can also influence nutrient solution management. For example, recirculating systems may require more frequent monitoring and adjustments due to nutrient depletion, while non-recirculating systems may need less frequent changes.
By carefully considering these factors and tailoring your nutrient solution to meet your plant’s specific needs, you can provide the optimal nutrition for healthy growth and achieve the best results in your hydroponic garden. Regular observation, research, and adjustment are key to successful nutrient management in hydroponics.
Nutrient Management and Monitoring in Hydroponics
Once you have formulated your nutrient solution, it’s important to monitor and manage its composition. Regularly testing the pH and electrical conductivity (EC) of your nutrient solution allows you to maintain the ideal range for optimal nutrient uptake. Additionally, monitoring the nutrient levels in your solution helps prevent deficiencies or toxicities. By establishing a nutrient management routine and keeping a close eye on your plants, you can make the necessary adjustments to maintain a healthy and productive hydroponic system.

Absolutely! Nutrient management and monitoring are critical aspects of successful hydroponic gardening. Here are some key points to consider for effective nutrient management in your hydroponic system:
1. pH Monitoring:
Regularly check the pH level of your nutrient solution using a pH meter or pH test kit. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range (around 5.5 to 6.5) for optimal nutrient uptake. pH levels that are too high or too low can lead to nutrient imbalances and deficiencies, even if the nutrients are present in the solution. Adjust the pH as needed using pH up (usually potassium hydroxide) or pH down (usually phosphoric acid) solutions.
2. EC Monitoring:
Electrical Conductivity (EC) is a measure of the concentration of dissolved salts (i.e., nutrients) in the nutrient solution. Monitoring EC levels gives you an indication of the nutrient strength in the solution. Different plant species have varying tolerance levels to EC, and the optimal range will depend on the specific plants you are growing and their growth stage. Adjust the EC by adding more nutrient solution to dilute it or by increasing nutrient concentrations when necessary.
3. Regular Testing:
Regularly test the nutrient levels in your solution to ensure that essential nutrients are present in the correct ratios. Commercial nutrient test kits or laboratory testing services can provide detailed information about nutrient concentrations, allowing you to adjust the solution accordingly. Address any nutrient deficiencies promptly to prevent adverse effects on plant growth.
4. Nutrient Solution Changes:
Over time, as plants uptake nutrients and the solution becomes depleted, you may need to replace or refresh the nutrient solution. The frequency of solution changes will depend on your hydroponic system type, plant type, and nutrient concentration. Some systems, like recirculating ones, may require more frequent nutrient solution changes to maintain the desired nutrient levels.
5. Plant Observation:
Regularly observe your plants for any signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities. Common symptoms include leaf discoloration, wilting, stunted growth, and unusual leaf patterns. Early detection of these issues can help you adjust the nutrient solution before the problems become severe.
6. Record Keeping:
Maintain a record of your nutrient management activities, including pH and EC readings, nutrient solution changes, and any adjustments made. Keeping track of this information helps you understand how your plants respond to different nutrient concentrations and environmental conditions, allowing you to make more informed decisions in the future.
By implementing a robust nutrient management and monitoring routine, you can optimize nutrient delivery to your plants, minimize nutrient-related issues, and maintain a healthy and productive hydroponic system. Regular attention and adjustments will ensure that your plants receive the ideal nutrition they need for vigorous growth and abundant yields.
Common Misconceptions about Hydroponic Nutrients
There are several misconceptions surrounding hydroponic nutrients that can lead to confusion among growers.

Let’s address a few more common misconceptions:
1. Hydroponic Plants Don’t Need Nutrients: As you mentioned, this is a prevalent misconception. Some people assume that since hydroponic plants grow without soil, they might not require nutrients. However, plants in hydroponic systems depend entirely on the nutrient solution provided to them for their growth and development. Without a properly balanced nutrient solution, hydroponic plants can suffer from nutrient deficiencies and fail to thrive.
2. Nutrient Solutions Are All the Same: Not all nutrient solutions are created equal. Different plant species have varying nutrient requirements, and the nutrient solution composition needs to be adjusted based on the specific needs of the plants being grown. Additionally, plants in different growth stages may have different nutrient demands, requiring adjustments to the solution as they progress from vegetative to flowering phases.
3. Organic Nutrients Are Always Better: While organic nutrients have their advantages, as we discussed earlier, they may not always be the best option for every hydroponic system. Organic nutrient sources may come with potential risks, such as introducing pathogens or clogging irrigation systems. Synthetic nutrients can be formulated to provide precise nutrient ratios and immediate availability, which can be beneficial for certain crops and growth stages.
4. Nutrients Can Be Used Indefinitely: Nutrient solutions in hydroponic systems do not last indefinitely. As plants take up nutrients, the solution becomes depleted, leading to nutrient imbalances and deficiencies. Regular monitoring and periodic solution changes are necessary to ensure that plants receive the required nutrients in the right proportions.
5. More Nutrients Lead to Better Growth: Providing excessive nutrients does not necessarily translate to better growth. In fact, over-fertilization can lead to nutrient toxicities and negatively impact plant health. It’s crucial to provide nutrients in the correct ratios and concentrations to avoid nutrient imbalances and potential harm to the plants.
6. Hydroponic Nutrients Are Cost-Prohibitive: While there are premium nutrient brands available, there are also more affordable nutrient options that can yield excellent results. The cost of hydroponic nutrients can vary depending on the brand and formulation, but it’s possible to find suitable nutrient solutions within a reasonable budget.
Understanding these misconceptions and getting informed about hydroponic nutrients will empower growers to make well-informed decisions, optimize nutrient management, and create a successful hydroponic gardening experience. Each hydroponic system and plant type may have specific nutrient requirements, and customizing the nutrient solution to meet those needs is crucial for achieving healthy and productive plant growth.
Recommended Nutrient Brands for Hydroponics
With numerous nutrient brands available on the market, it can be overwhelming to choose the right one for your hydroponic garden. Some well-established brands known for their quality and effectiveness include General Hydroponics, Advanced Nutrients, Fox Farm, and Botanicare. These brands offer a range of nutrient solutions tailored to different plant types and growth stages. It’s important to research and consider factors such as nutrient composition, reputation, and user reviews to find the best nutrient brand that suits your needs and budget.

We’ve mentioned some reputable nutrient brands that are well-known in the hydroponic gardening community. Here’s a brief overview of the brands we mentioned, along with some additional considerations:
1. General Hydroponics:
General Hydroponics (GH) is a well-established brand with a wide range of nutrient solutions suitable for various hydroponic systems and plant types. They offer both liquid and powdered nutrient formulations, including the popular Flora series. GH is known for its consistent quality and effectiveness, making it a reliable choice for many hydroponic growers.
2. Advanced Nutrients:
Advanced Nutrients is another well-regarded brand that focuses on providing high-quality and specialized nutrient solutions for hydroponic and soil-based cultivation. They offer a wide range of products designed to enhance specific growth stages and optimize plant performance. Advanced Nutrients is often favored by experienced growers looking for precise nutrient control.
3. Fox Farm:
Fox Farm is known for its organic-based nutrient formulations. They offer a selection of liquid nutrients tailored for different growth stages and plant types. Fox Farm nutrients are popular among growers who prefer organic gardening practices and seek natural-based nutrient solutions.
4. Botanicare:
Botanicare is a brand that provides a variety of nutrient options, including both one-part and two-part nutrient solutions. They are well-regarded for their easy-to-use and reliable products, suitable for various hydroponic setups.
5. Considerations:
When selecting a nutrient brand, consider the following factors:
- Plant Type: Ensure that the brand’s nutrient formulations align with the specific plant types you are growing.
- Growth Stage: Some brands offer nutrients designed for specific growth stages, such as vegetative or flowering, which can be beneficial for optimizing plant development.
- Nutrient Composition: Look into the nutrient ratios and the presence of essential elements like macronutrients and micronutrients to ensure comprehensive nutrition for your plants.
- pH Stability: Some nutrient solutions are formulated to maintain a stable pH range, which can simplify pH adjustments in your hydroponic system.
- User Reviews: Reading reviews and feedback from other growers can provide insights into the effectiveness and reliability of a particular brand’s nutrients.
Ultimately, the best nutrient brand for your hydroponic garden will depend on your specific requirements, preferences, and budget. It’s always a good idea to start with a reputable and well-established brand, but experimentation and observation in your own setup will help you determine which nutrient solution works best for your plants and hydroponic system.
Conclusion
Absolutely! Mastering nutrient management is indeed a key factor in achieving successful and productive hydroponic gardening. By understanding the essential roles of nutrients, their specific functions, and the various nutrient options available, you can create an optimized and balanced nutrient solution tailored to the needs of your plants.
Regular monitoring of pH, EC, and nutrient levels, as well as vigilant observation of plant health, allows you to make timely adjustments to maintain an optimal nutrient environment. Using recommended nutrient brands known for their quality and effectiveness can further enhance your hydroponic gardening experience.
With the knowledge gained from this comprehensive guide on nutrients for hydroponics, you are well-equipped to embark on your hydroponic gardening journey with confidence. By applying these principles and practices, you can nurture healthy, vibrant plants and enjoy bountiful harvests. Happy growing and best of luck in your hydroponic adventures!






